EPFL scientists have carried out a genomic and evolutionary study of a large and enigmatic family of human proteins, to demonstrate that it is responsible for harnessing the millions of transposable elements in the human genome. The work reveals the largely species-specific gene-regulatory networks that impact all of human biology, in both health and disease.
Latest Biology Articles, News & Current Events
For the first time, researchers from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and their collaborators have been able to identify in human cancers two characteristic patterns of DNA damage caused by ionising radiation. These fingerprint patterns may now enable doctors to identify which tumours have been caused by radiation, and investigate if they should be treated differently.
| Full article | September 12, 2016 06:22 PM | 585690 views |
In a first-of-its-kind look at human kidney development, researchers at The Saban Research Institute of Children's Hospital Los Angeles have isolated human nephron progenitor (NP) cells. Their results, published online in the journal Stem Cell Translational Medicine, will help scientists understand how these progenitor cells become renal cells in the developing fetus, and possibly offer a future way to foster renal regeneration after chronic kidney failure or acute injury.
| Full article | September 12, 2016 06:22 PM | 531424 views |
Scientists from the Senckenberg and the Giraffe Conservation Foundation have analysed the genetic relationships of all major populations of giraffe in the wild. The large study on the genetic makeup of giraffe, published today in Current Biology, shows that there are four distinct giraffe species. Until now, only one giraffe species had been recognized. The unexpected results are based on analyses using several nuclear marker genes of more than 100 animals. The new insights are set to improve protection efforts of these endangered animals in Africa.
| Full article | September 8, 2016 07:41 PM | 495359 views |
In research published online today in Science, a team of scientists describe a new therapeutic strategy to target a hidden Achilles' heel shared by all known types of Ebola virus. Two antibodies developed with this strategy blocked the invasion of human cells by all five ebolaviruses, and one of them protected mice exposed to lethal doses of Ebola Zaire and Sudan, the two most dangerous. The team included scientists from Albert Einstein College of Medicine, U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID), Integrated Biotherapeutics, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, and The Scripps Research Institute.
| Full article | September 8, 2016 07:41 PM | 485505 views |
Stanford University School of Medicine scientists have identified a brain circuit that's indispensable to the sleep-wake cycle. This same circuit is also a key component of the reward system, an archipelago of interconnected brain clusters crucial to promoting behavior necessary for animals, including humans, to survive and reproduce.
| Full article | September 5, 2016 06:38 PM | 486489 views |
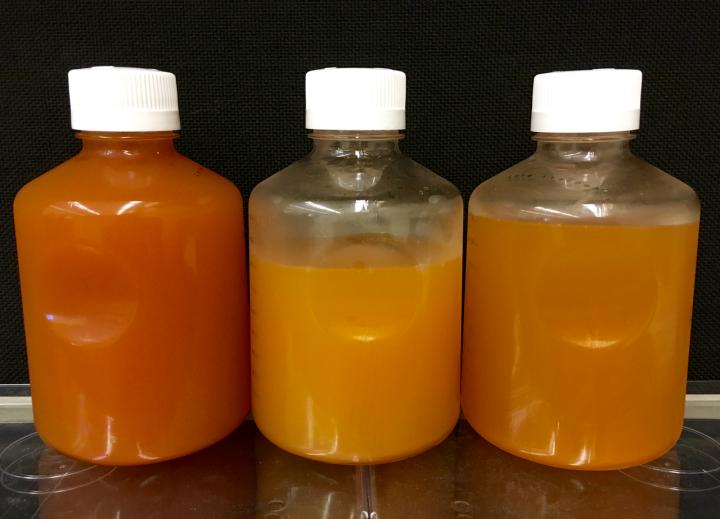

Ohio State University researchers and their colleagues have identified a new genus of bacteria living inside hydraulic fracturing wells. Researchers analyzing the genomes of microorganisms living in shale oil and gas wells have found evidence of sustainable ecosystems taking hold there--populated in part by a never-before-seen genus of bacteria they have dubbed "Frackibacter."
| Full article | September 5, 2016 06:38 PM | 438686 views |
Biochemists at the University of California San Diego have uncovered patterns in the outer protein coat of group A Streptococcus that could finally lead to a vaccine against this highly infectious bacteria--responsible for more than 500,000 deaths a year, including toxic shock syndrome and necrotizing fasciitis or "flesh-eating disease."
| Full article | September 5, 2016 06:38 PM | 406132 views |
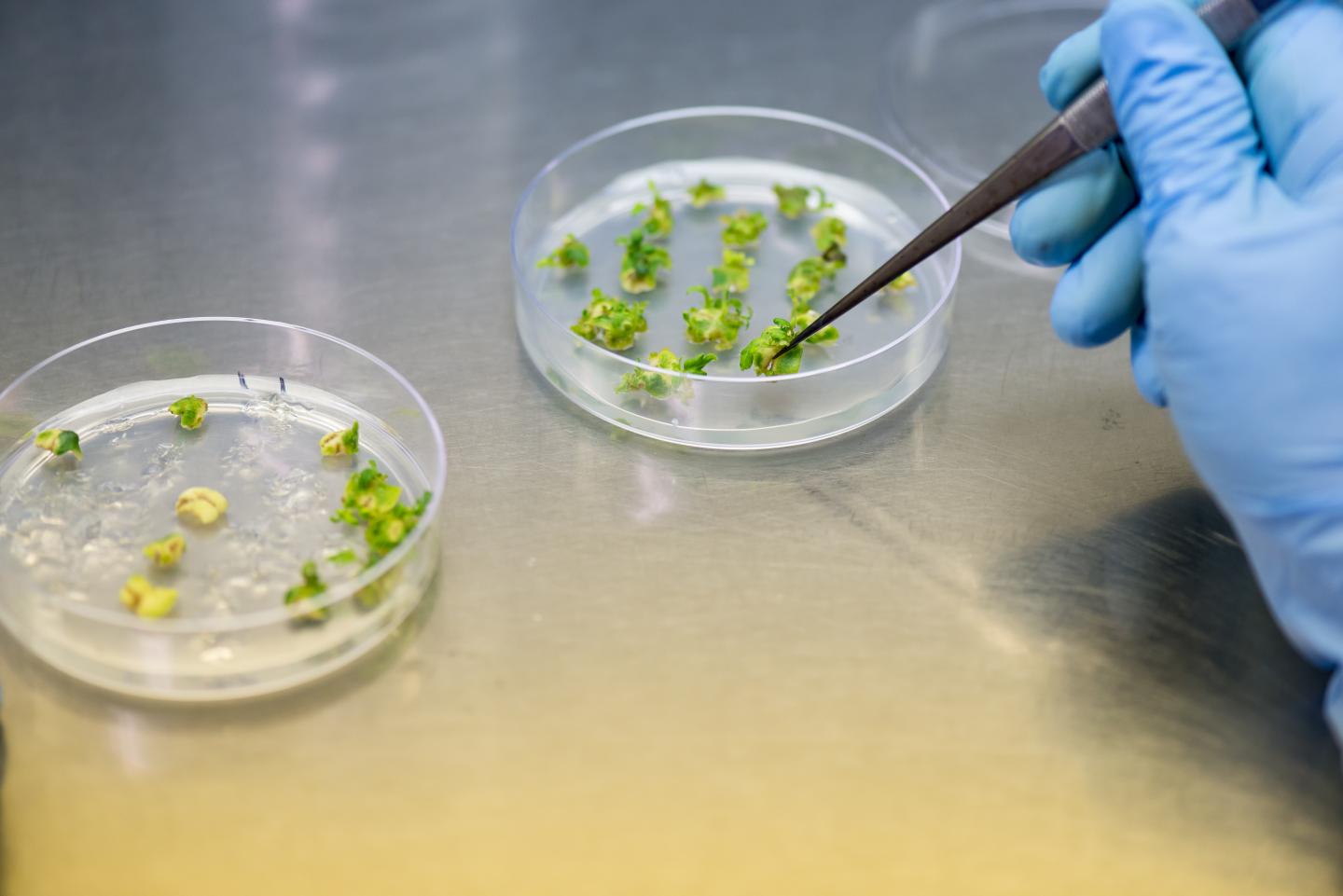

A researcher transfers tomato plantlets from a plate of regeneration medium. Tomatoes are already an ideal model species for plant research, but scientists at the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI) just made them even more useful by cutting the time required to modify their genes by six weeks.
| Full article | August 30, 2016 05:36 PM | 407823 views |
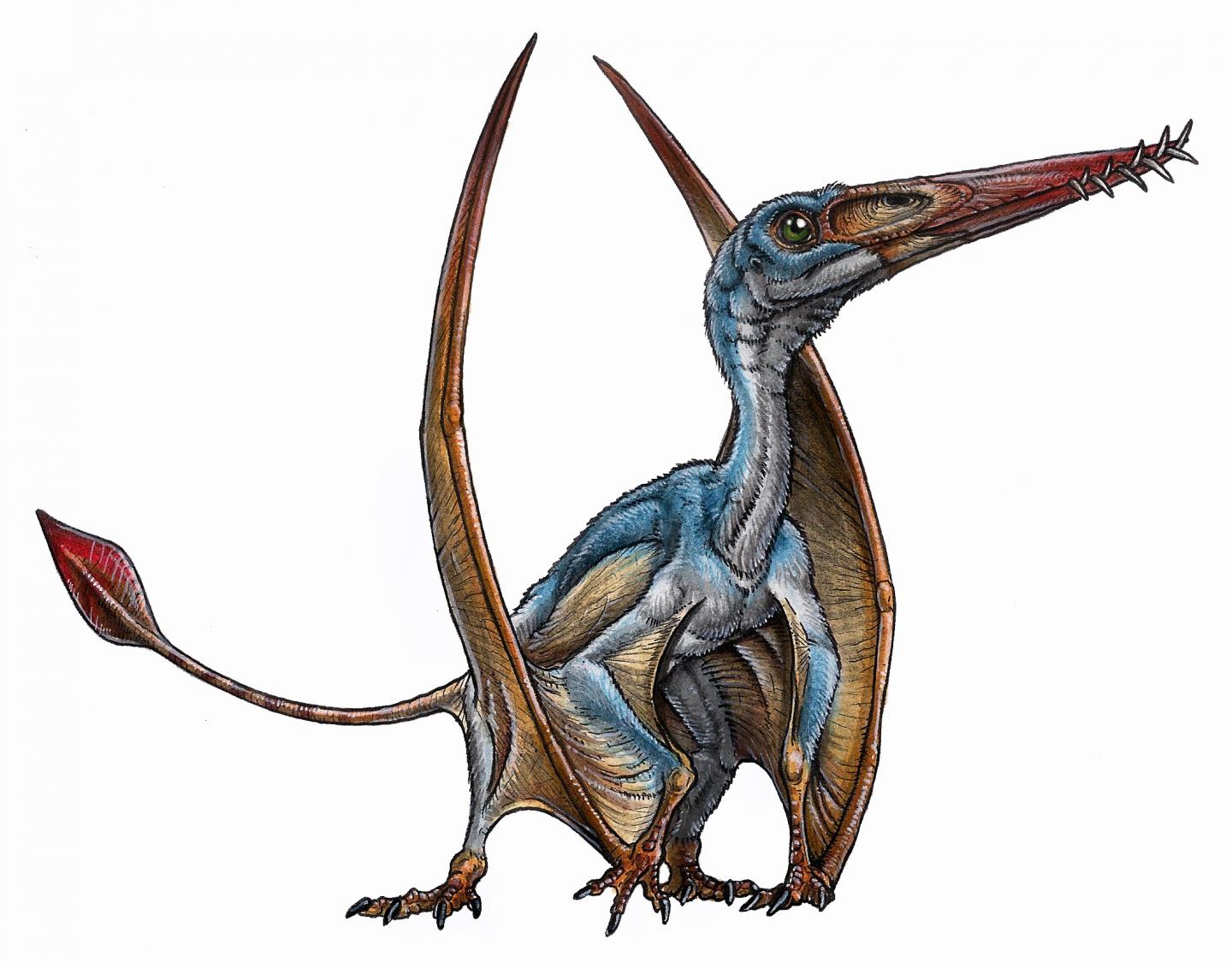

This is a paleoartist's reconstruction of a ptesosaur. Scientists today announced the discovery of a new species of pterosaur from the Patagonia region of South America. The cranial remains were in an excellent state of preservation and belonged to a new species of pterosaur from the Early Jurassic. The researchers have named this new species 'Allkauren koi' from the native Tehuelche word 'all' for 'brain', and 'karuen' for 'ancient'.
| Full article | August 30, 2016 05:36 PM | 412819 views |
Researchers at Houston Methodist have developed an artificial intelligence (AI) software that reliably interprets mammograms, assisting doctors with a quick and accurate prediction of breast cancer risk. According to a new study published in Cancer (early online Aug. 29), the computer software intuitively translates patient charts into diagnostic information at 30 times human speed and with 99 percent accuracy.
| Full article | August 29, 2016 06:12 PM | 63729 views |
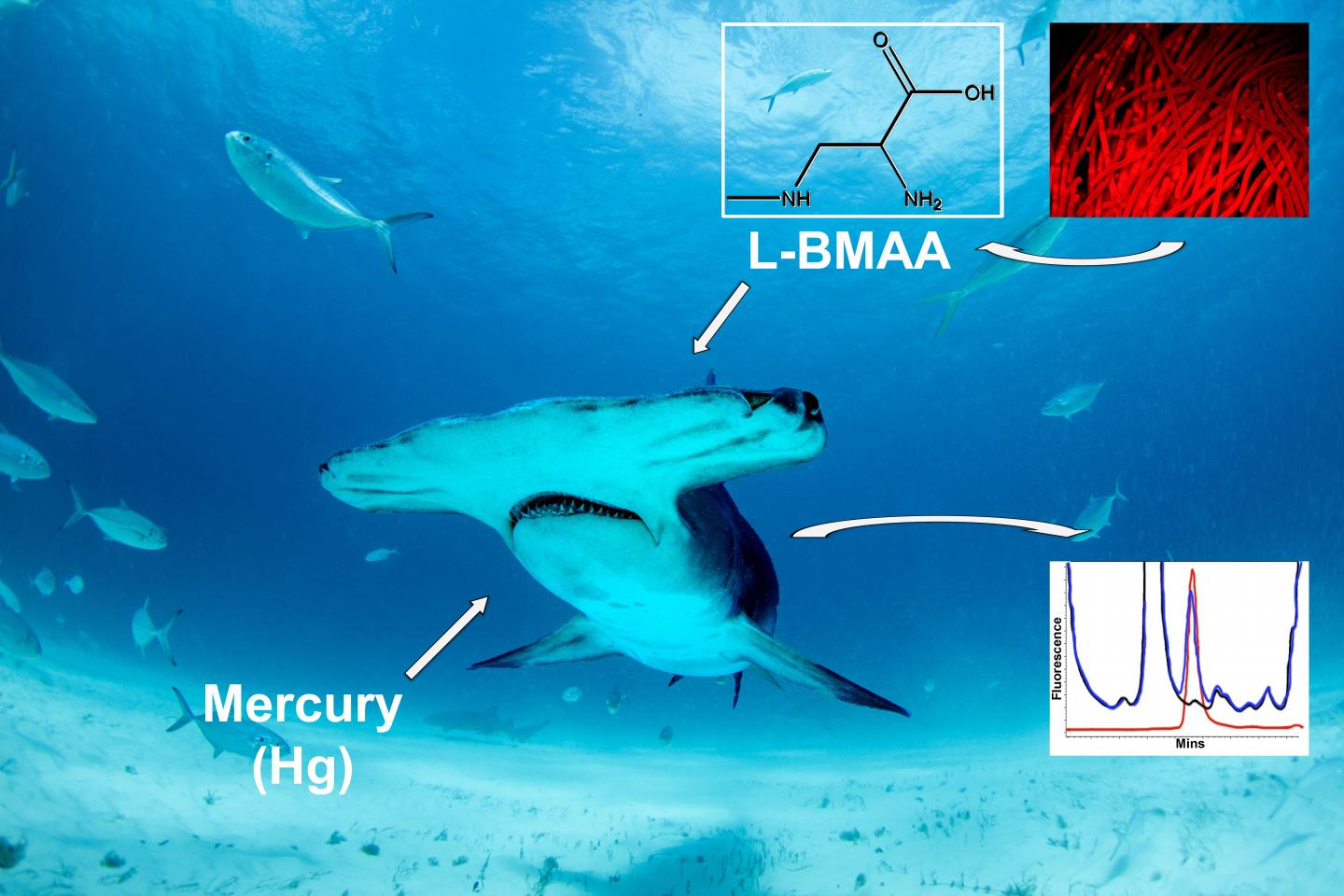
Cyanobacterial neurotoxin β-N-methylamino-L-alanine (BMAA) and Mercury are detected in sharks from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. In a new study, University of Miami (UM) scientists found high concentrations of toxins linked to neurodegenerative diseases in the fins and muscles of 10 species of sharks. The research team suggests that restricting consumption of sharks can have positive health benefits for consumers and for shark conservation, since several of the sharks analyzed in the study are threatened with extinction due to overfishing.
| Full article | August 29, 2016 06:12 PM | 206071 views |
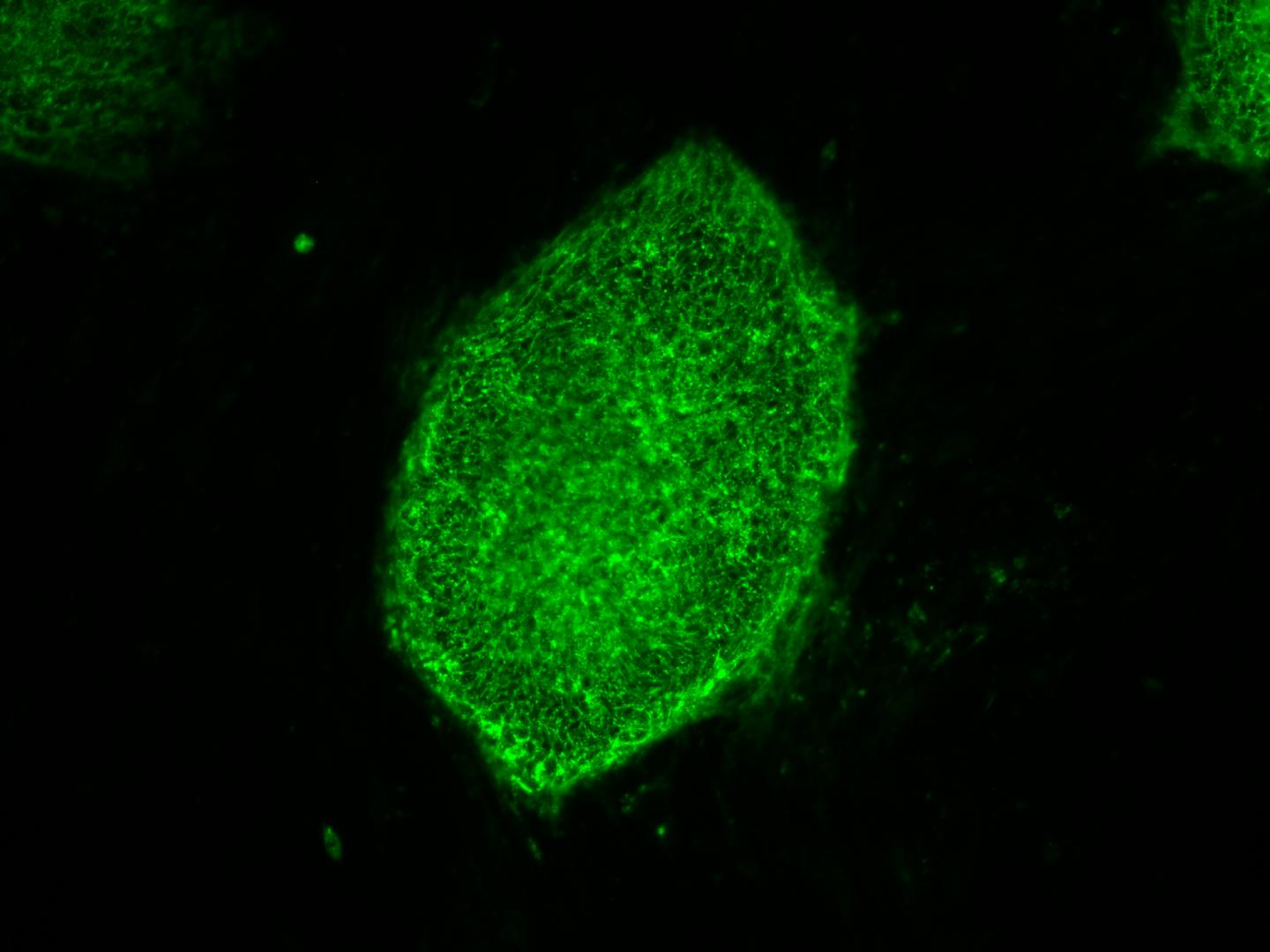
This image shows induced pluripotent stem cells expressing a characteristic cell surface protein called SSEA4 (green). A research team including developmental biologist Stephen A. Duncan, D. Phil., SmartStateTM Chair of Regenerative Medicine at the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC), has found a better way to purify liver cells made from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Their efforts, published August 25, 2016 in Stem Cell Reports, will aid studies of liver disease for the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)'s $80 million Next Generation Genetic Association Studies (Next Gen) Program. The University of Minnesota (Minneapolis) and the Medical College of Wisconsin (Milwaukee) contributed to the study.
| Full article | August 29, 2016 06:12 PM | 57519 views |
In a very severe, genetic form of microcephaly, stem cells in the brain fail to divide, according to a new Columbia University Medical Center study that may provide important clues to understanding how the Zika virus affects the developing brain.
| Full article | August 24, 2016 07:26 PM | 56656 views |
Previous Biology Articles & News
- In some genetic cases of microcephaly, stem cells fail to launch
- Yale team discovers how Zika virus causes fetal brain damage
- Scientists uncover the way a common cell enzyme alerts the body to invading bacteria
- Arctic gives clues on worst mass extinction of life
- Calcium channel blockers caught in the act at atomic level
Search Bio News Net
Free Biology Newsletter
- Flexibility That A.C.A. Lent to Work Force Is Threatened by...International Herald Tribune
- Bacteria Behind Legionnaires’ Disease Found at New York Police StationInternational Herald Tribune
- Prescription Price Crisis? 28 Million Americans See Spike in Drug...MSNBC.com: Health
- Seizing on Opioid Crisis, a Drug Maker Lobbies Hard for...International Herald Tribune
- Republicans are taking a big political risk on health careAP Health News
- Why We're So Divided Over Saving WolvesNational Geographic News

