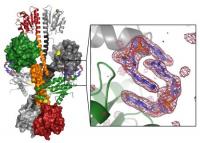
Tetrameric assembly of the response regulator diguanylate cyclase WspR from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The inset shows a close-up of cyclic di-GMP bound to the inhibitory site Bacteria are particularly harmful to human health when they band together to form a biofilm—a sheet composed of many individual bacteria glued together—because this can allow them to escape from both antibiotics and the immune system of their host. It is thought that most chronic infections are caused by bacterial biofilms, and a paper published in this week’s PLoS Biology explores the signalling system that causes bacteria to team up in this way.
Pseudomonas is the pathogen that forms biofilms in the lungs of people with cystic fibrosis. The new paper, from Holger Sondermann and colleagues, identifies a novel kind of control system for bacterial signalling. Bacteria form a biofilm when the concentration of a molecule called c-di-GMP gets above a certain threshold. Sondermann et al. have determined the structure of the enzyme that makes c-di-GMP. The enzyme is called WspR in Pseudomonas, and the way WspR is controlled in the cell is the focus of their paper.
The authors determined the crystal structure of WspR and followed up with biochemical analysis of the enzyme. This work showed that WspR exists in an active form that produces c-di-GMP and is then bound by c-di-GMP and forced into an inactive form. The study therefore reveals a finely balanced equilibrium between the synthesis and degradation of this key player in biofilm formation.
New approaches to controlling the behavior of bacteria responsible for chronic infections can be envisaged. Because the signalling molecules involved in biofilm formation, such as c-di-GMP, are uniquely found in bacteria, the authors hope that there is potential for new therapeutic treatments based on this work; if you interrupted this bacterial signalling it would have no negative effect on the human host but could be devastating for the bacteria.
Source : Public Library of Science
 Print Article
Print Article Mail to a Friend
Mail to a Friend
